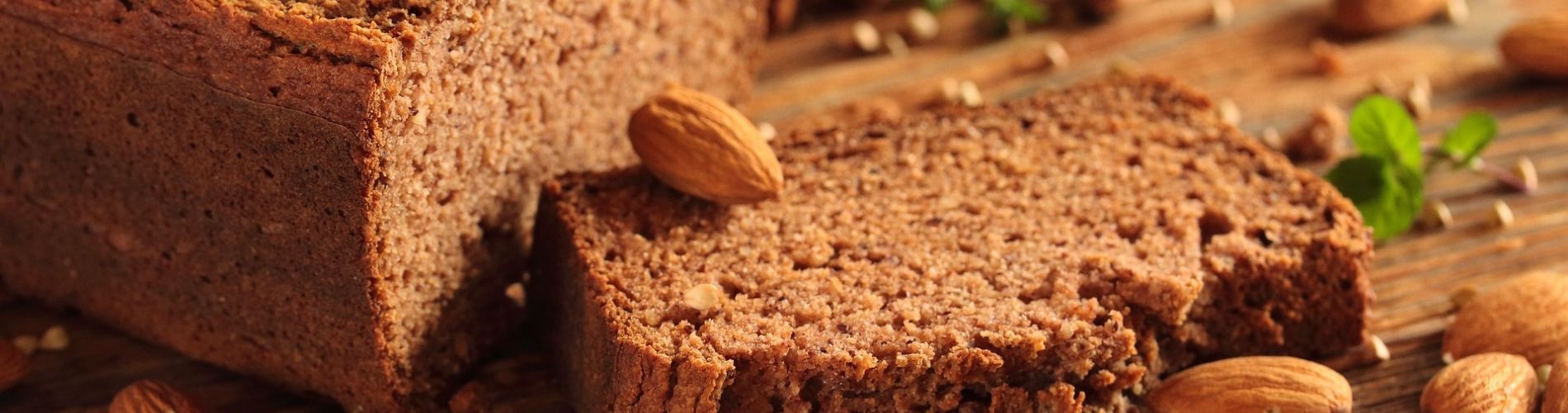
Nowadays you can find lots of groceries in the supermarket with the label gluten-free. The same goes for the menus at restaurants. Most of the restaurants are offering gluten-free options.
What is gluten?
Gluten is a mixture of several proteins that can be found in different types of cereals. You can find gluten for example in spelt, rye, barley and oats. Gluten has the function of glue and is keeping the bread together. There are also gluten-free cereals like millet.
In the last couple of years, more and more people changed their nutrition and have given up gluten. You often hear that people have a gluten-allergy or have a gluten intolerance. What exactly is the meaning of these things and what effect do these diseases have on the body?
Gluten allergy (celiac disease)
The gluten allergy is also called celiac disease. The body doesn’t tolerate gluten. This leads to the point that the body is building antibodies against gluten. These antibodies also destroy the mucous membrane in the small intestines. This can lead to an under-supply of important nutrients.
The celiac disease can be treated but not healed. Not the cause, but only the symptoms can be treated for the celiac disease and the disease can be inherited. The symptoms of the celiac disease are quite clear. These symptoms are diarrhea, stomach pain, losing weight and nutrient-deficiency.
Gluten Intolerance
A gluten intolerance is different to a gluten allergy. The symptoms of it are not as clear and don’t seem to have a connection to a food intolerance. In addition to the typical symptoms like stomach pain and diarrhea, other symptoms can appear like headaches, migraines, sleep disorders, exhaustion, concentration disorders, mood changes, and muscle pain. In contrast to the celiac disease, the patients have a good chance that the intolerance regresses after a few years.
Diagnosis
Often the diagnoses can be quite difficult since doctors are thinking of gluten intolerance for certain symptoms. Often the patients are falsely diagnosed with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Part of the problem is that these symptoms don’t appear right after eating, but only a few days later, so it is difficult to see the connection.
It is recommended to change the nutrition to gluten-free for a longer period of time to see if the symptoms get better. After a bit of time, the gluten will be brought back to the nutrition plan and when the symptoms come back again, then the chances are pretty good that it is a gluten intolerance.
A gluten intolerance can have quite an impact since this can lead to a few other diseases like osteoporosis, type-1-diabetes, migraines, arthritis, and epilepsy. Thankfully there are lots of gluten-free products available these days and it is possible to have a balanced nutrition without gluten in it.
It can often be difficult to get a proper diagnosis because 8-10% of gluten/celiac disease patients do not respond positively to conventional tests. The POC * it Allergy test 3-in-1 tests for both IgA or IgG antibodies to tTG in a test and gives you reassurance.