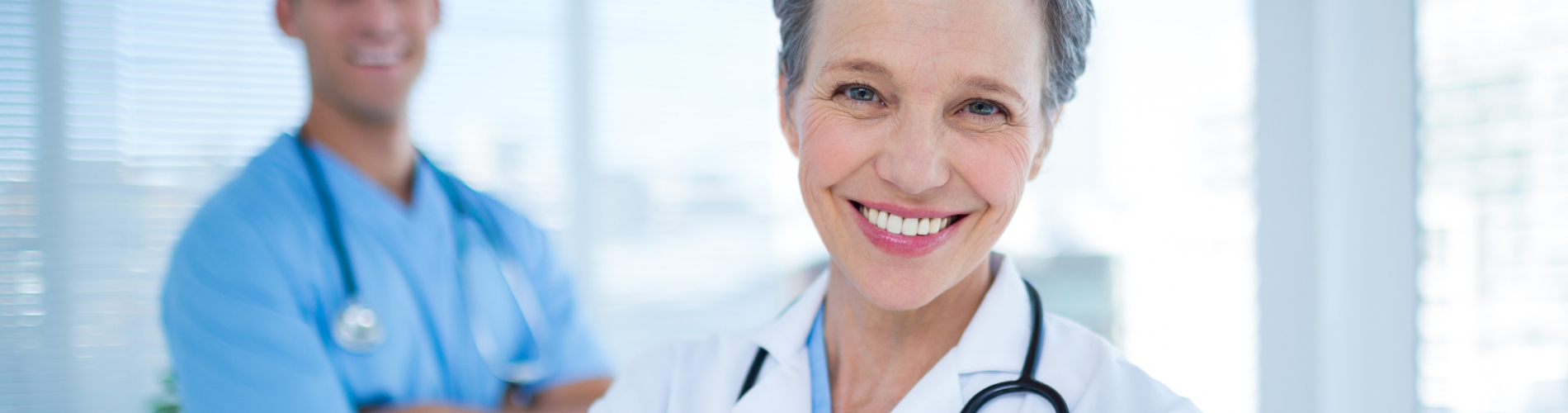
The diabetes scourge is evidently a serious issue individuals and governments should take more serious and not with levity. With as many as 2.2 million deaths attributed to diabetes in 2015 worldwide and over 422 million others suffering from the disease presently (put at 108 million in 1980), it is evident this is becoming endemic and alarming.
The good news, however, is that simply relying on knowledge about your blood sugar level on a daily basis can save your life. Self-monitoring how high or low the blood glucose is in the body is crucial to how you manage the disease.
Whether it is Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, making blood glucose-monitoring a daily routine also helps the sufferer recognize how other factors like stress, illness, food choice, exercise, and general lifestyle affect the management of the disease.
Glucose is a simple sugar which supplies the energy needed by the body for physical and mental activities. Derived from the complete digestion of carbohydrate foods, glucose is the primary sugar present in the human blood; it is at this point that it is called blood glucose or blood sugar.
While it is very important to have an abundance of energy from blood glucose, care needs to be taken in order to ensure that a healthy quantity of sugar in the blood system is maintained. The abnormal quantity, on the other hand, could be either a very high blood glucose level or a very low one.
Any of these anomalies can result in unhealthy and serious consequences in a person. To avoid having to suffer from the effects of having too much or too little of blood sugar, doctors advise the regular observation of glucose in the blood by keeping an up-to-date record of our blood sugar levels. This is easily done with a blood glucose monitoring device.
Blood Glucose Monitoring Indication
The goal of blood glucose monitoring is to protect persons who may have or who are having problems caused by an abnormal blood glucose condition. Essentially, children, adolescents, and adults with diabetes mellitus type 1 or type 2 should have their blood sugar levels observed and kept in check from time to time. Also, aged persons, pregnant women, and persons with medical challenges that involve vital organs of the body should keep close observations of their blood glucose levels. It can be easily done by oneself, even at home.
Why is Blood Glucose Monitoring Important?
Generally, closely observing for changes in the blood sugar is for the benefit of staying in good health. Specifically, it can assist a person in:
- Finding out how high or low his blood sugar level is
- Interpreting the effect of foods and activities on his blood sugar level
- Knowing how stress, disease, and other harsh factors affect the blood sugar level
For diabetes mellitus patients, keeping a regular schedule of the blood sugar level helps in:
- Keeping track of the effect that medicines for diabetes have on the level of blood sugar
- Determining how well they are progressing in achieving health through the treatment of diabetes
- Discovering problems with insulin medications
How Often Should The Blood Glucose Level Be Monitored?
A person may not know if his blood sugar level is abnormal until a blood glucose test is carried out on his blood sample. This is usually carried out by a doctor or any other healthcare professional in the hospital.
The result of the blood sugar test will determine how often the person should monitor his blood glucose level. In diabetic conditions, the frequency of monitoring differs depending on the type of diabetes a person has and his treatment plan as recommended by his doctor.
Blood glucose monitoring in persons with diabetes mellitus type 1 can be done as often as 10 times a day. The number of times can increase when they become sick or have their medications changed with the consent of their doctors.
Persons having diabetes mellitus type 2 managed with insulin do not need to monitor as often as type 1 patients. Theirs could be as few as twice daily, before breakfast and dinner. Daily monitoring of blood glucose can be ruled out for type 2 diabetic persons who do not rely on insulin medications to manage their diabetic conditions.
Blood Glucose Monitoring Values
Depending on factors such as age and existing medical conditions, the values obtained from observing the level of sugar in the blood could vary. In non-diabetic persons with no existing health challenge, blood glucose level checked eight hours before consuming any food in the morning should be less than 100 mg/dL (milligrams per decilitre); it should be less than 140 mg/dL when it is checked two hours after a meal.
For diabetic persons, their target blood sugar levels should be:
- Between 80 and 130 mg/dL before meals
- Less than 180 mg/dL two hours after meals
Aged persons (60 years and above), and those who have health conditions that affect their hearts, lungs, kidneys or their ability to feel when their blood levels have gone low should aim at attaining a blood glucose level between 100 and 140 mg/dL.
Pregnant women should maintain a fasting blood sugar level less than 95 mg/dL.
Guidelines for Monitoring Blood Glucose Level
Basically, the blood glucose level can be accurately kept in check with the aid of a blood glucose monitoring device. Test strips and a lancet (for pricking of the fingertip) are required when using the device to determine the blood glucose level.
To be able to get the right results, the instructions on the device needs to be followed appropriately.
Below are the general guidelines for using the instrument:
- Ensure your hands are washed and dried properly
- Fit in a test strip into the device
- With the help of the lancet, prick the side of your fingertip. (Note that the blood sample from the fingertip gives a more precise result than the blood from any other part of the body)
- Massage the pricked area until there is a visible drop of blood formed
- Touch and firmly hold the edge of the test strip with your perforated fingertip
Blood Glucose Monitoring Recommendations
When using a blood glucose monitoring device, it is important to record the results alongside the date and time of the testing. This can be done in a book specifically dedicated to monitoring blood sugar or documented electronically in the computer. Your doctor may require a log of the results during your scheduled appointments.
There have been concerns of late over self-monitoring of blood glucose level. One of such matters relates to the calibration of the monitoring device sold in pharmacies. A confusing calibration can lead to errors in the recording which, in diabetes patients, can cause a mistreatment of the disease condition.
To prevent that from happening, one has to be careful while purchasing a blood glucose monitoring device. There should be a clearly stated standard of measurement for the whole blood or the plasma on the device. Additionally, the range of the value of blood glucose it can measure should be indicated visibly on the instrument.
Conversion formulas from a unit to another unit should also be well-placed on the instructional leaflet of the device. It allows for the easy changeover of result values to preferred units – depending on one’s region.
This is where Palliance comes in. For more than 20 years the people at Palliance have worked with diagnostics and for more ten years, we have proudly supplied pharmacy chains with high-quality self-testing and monitoring devices that are CE and FDA approved. Palliance now enters into collaboration with one of the major global suppliers of blood glucose and cholesterol monitoring and will shortly present major news about this.
Check out more information on the blog at Palliance.eu or https://pocit.de in the time to come.